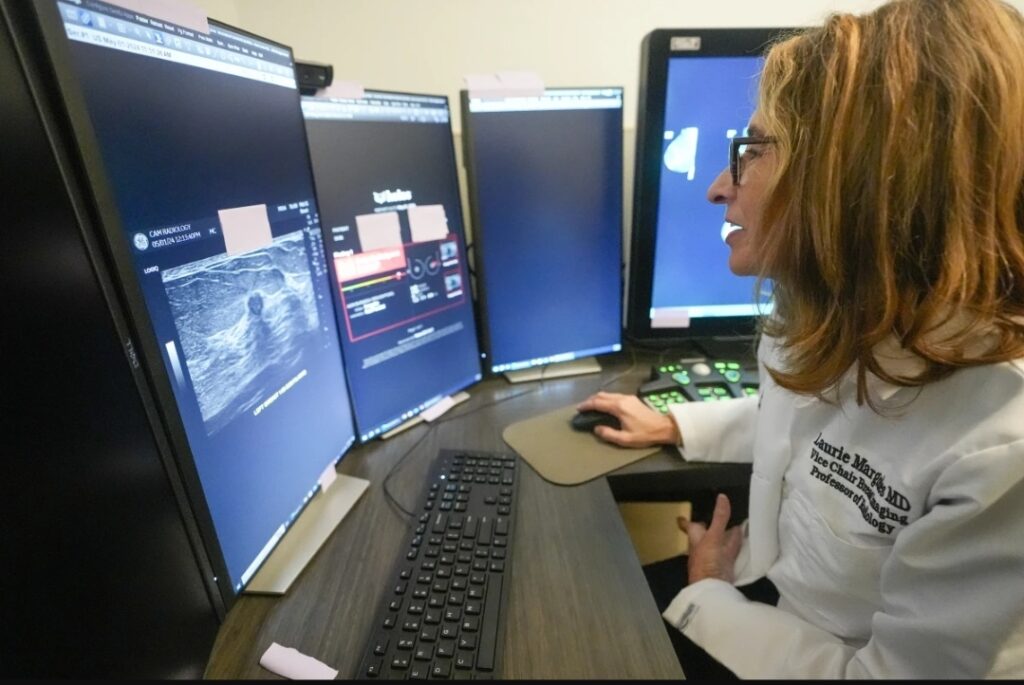
Dr. Laurie Margolies demonstrates the Koios DS Sensible Ultrasound software program, Wednesday, Might 8, 2024, at Mount Sinai hospital in New York. The breast imaging AI is used to get a second opinion on mammography ultrasounds. “I’ll inform sufferers, ‘I checked out it, and the pc checked out it, and we each agree,’” Margolies stated. “Listening to me say that we each agree, I feel that offers the affected person an excellent higher stage of confidence.” (AP Picture/Mary Altaffer)
WASHINGTON (AP) — How good would an algorithm need to be to take over your job?
It’s a brand new query for a lot of staff amid the rise of ChatGPT and different AI applications that may maintain conversations, write tales and even generate songs and pictures inside seconds.
For docs who evaluate scans to identify most cancers and different ailments, nevertheless, AI has loomed for a couple of decade as extra algorithms promise to enhance accuracy, pace up work and, in some instances, take over whole elements of the job. Predictions have ranged from doomsday situations wherein AI absolutely replaces radiologists, to sunny futures wherein it frees them to give attention to essentially the most rewarding points of their work.
That stress displays how AI is rolling out throughout well being care. Past the know-how itself, a lot relies upon upon the willingness of docs to place their belief — and their sufferers’ well being — within the palms of more and more refined algorithms that few perceive.
Even inside the discipline, opinions differ on how a lot radiologists ought to be embracing the know-how.
“A few of the AI methods are so good, frankly, I feel we ought to be doing them now,” stated Dr. Ronald Summers, a radiologist and AI researcher on the Nationwide Institutes of Well being. “Why are we letting that info simply sit on the desk?”
Summers’ lab has developed computer-aided imaging applications that detect colon most cancers, osteoporosis, diabetes and different situations. None of these have been extensively adopted, which he attributes to the “tradition of drugs,” amongst different components.
Radiologists have used computer systems to reinforce photos and flag suspicious areas because the Nineties. However the newest AI applications can go a lot additional, deciphering the scans, providing a possible analysis and even drafting written reviews about their findings. The algorithms are sometimes skilled on thousands and thousands of X-rays and different photos collected from hospitals.
Throughout all of drugs, the FDA has OK’d greater than 700 AI algorithms to help physicians. Greater than 75% of them are in radiology, but simply 2% of radiology practices use such know-how, in response to one current estimate.
READ: AI can be in every single place in 2024
For all the guarantees from trade, radiologists see various causes to be skeptical of AI applications: restricted testing in real-world settings, lack of transparency about how they work and questions concerning the demographics of the sufferers used to coach them.
“If we don’t know on what instances the AI was examined, or whether or not these instances are just like the sorts of sufferers we see in our apply, there’s only a query in everybody’s thoughts as as to if these are going to work for us,” stated Dr. Curtis Langlotz, a radiologist who runs an AI analysis heart at Stanford College.
Up to now, all of the applications cleared by the FDA require a human to be within the loop.
In early 2020, the FDA held a two-day workshop to debate algorithms that might function with out human oversight. Shortly afterwards, radiology professionals warned regulators in a letter that they “strongly consider it’s untimely for the FDA to think about approval or clearance” of such methods.
However European regulators in 2022 accepted the primary absolutely automated software program that opinions and writes reviews for chest X-rays that look wholesome and regular. The corporate behind the app, Oxipit, is submitting its U.S. utility to the FDA.
The necessity for such know-how in Europe is pressing, with some hospitals dealing with monthslong backlogs of scans attributable to a scarcity of radiologists.
Within the U.S., that type of automated screening is probably going years away. Not as a result of the know-how isn’t prepared, in response to AI executives, however as a result of radiologists aren’t but comfy turning over even routine duties to algorithms.
READ: Rise of AI: 5 enterprise predictions in 2024
“We attempt to inform them they’re overtreating folks they usually’re losing a ton of time and sources,” stated Chad McClennan, CEO of Koios Medical, which sells an AI device for ultrasounds of the thyroid, the overwhelming majority of which aren’t cancerous. “We inform them, ‘Let the machine take a look at it, you (evaluate and) signal the report and be executed with it.’”
Radiologists are likely to overestimate their very own accuracy, McClennan says. Analysis by his firm discovered physicians viewing the identical breast scans disagreed with one another greater than 30% of the time on whether or not to do a biopsy. The identical radiologists even disagreed with their very own preliminary assessments 20% of the time, when viewing the identical photos a month later.
About 20% of breast cancers are missed throughout routine mammograms, in response to the Nationwide Most cancers Institute.
After which there’s the potential for value financial savings. On common, U.S. radiologists earn over $350,000 yearly, in response to the Division of Labor.
Within the close to time period, specialists say AI will work like autopilot methods on planes — performing necessary navigation features, however all the time underneath the supervision of a human pilot.
That strategy provides reassurances to each docs and sufferers, says Dr. Laurie Margolies, of Mount Sinai hospital community in New York. The system makes use of Koios breast imaging AI to get a second opinion on breast ultrasounds.
“I’ll inform sufferers, ‘I checked out it, and the pc checked out it, and we each agree,’” Margolies stated. “Listening to me say that we each agree, I feel that offers the affected person an excellent higher stage of confidence.”
The primary giant, rigorous research testing AI-assisted radiologists in opposition to these working alone give hints on the potential enhancements.
Preliminary outcomes from a Swedish research of 80,000 girls confirmed a single radiologist working with AI detected 20% extra cancers than two radiologists working with out the know-how.
In Europe, mammograms are reviewed by two radiologists to enhance accuracy. However Sweden, like different international locations, faces a workforce scarcity, with only some dozen breast radiologists in a rustic of 10 million folks.
Utilizing AI as a substitute of a second reviewer decreased the human workload by 44%, in response to the research.
Nonetheless, the research’s lead writer says it’s important {that a} radiologist make the ultimate analysis in all instances.
If an automatic algorithm misses a most cancers, “that’s going to be very unfavorable for belief within the caregiver,” stated Dr. Kristina Lang of Lund College.
The query of who might be held liable in such instances is among the many thorny authorized points which have but to be resolved.
One result’s that radiologists are prone to proceed double-checking all AI determinations, lest they be held answerable for an error. That’s prone to wipe out most of the predicted advantages, together with decreased workload and burnout.
Solely a particularly correct, dependable algorithm would permit radiologists to actually step away from the method, says Dr. Saurabh Jha of the College of Pennsylvania.
Till such methods emerge, Jha likens AI-assisted radiology to somebody who provides that can assist you drive by wanting over your shoulder and consistently mentioning every part on the street.
“That’s not useful,” Jha says. “If you wish to assist me drive then you definitely take over the driving in order that I can sit again and calm down.”
Learn Subsequent

